- home
- education
- science
- Minds-on Activities for Teaching Biology
- Next Generation Science Standards
- Remote Ready Biology Activities
- NGSS Biology Activities
- Hands-On Activities for Teaching Biology
- Teaching Climate Change
- Science Education
- Summer Institutes for K-12 Teachers 1995-2010
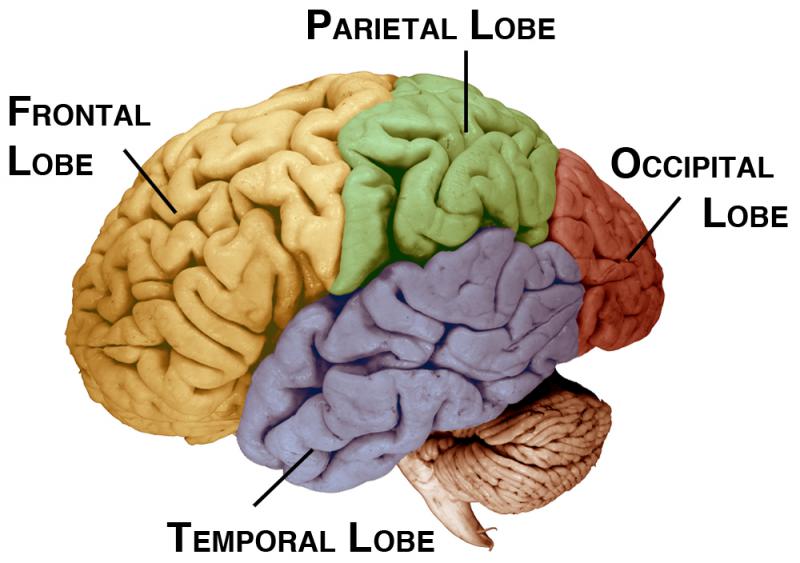
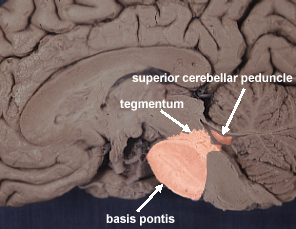
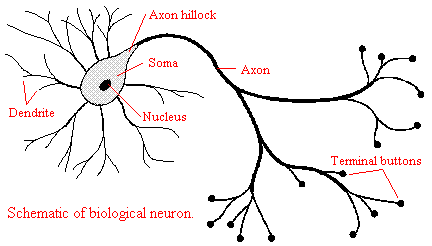
- Brain & Behavior
- Biology
- Science & Culture
- Complex Systems
- digital humanities
- play
- one world
 © Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
© Serendip® 1994 - All rights reserved. Privacy Policy